

You may remain awake but have medication to numb the surgery area (local anesthesia), or you may be unconscious during the surgery (general anesthesia). The surgery usually takes an hour to an hour and a half. Surgery to implant the vagus nerve stimulation device can be done on an outpatient basis, though some surgeons recommend staying overnight. Your doctor may have you start taking antibiotics before surgery to prevent infection. You may need blood tests or other tests to make sure you don't have any health concerns that might be a problem. What you can expect Before the procedureīefore surgery, your doctor will do a physical examination. You may need to stop taking certain medications ahead of time, and your doctor may ask you not to eat the night before the procedure.
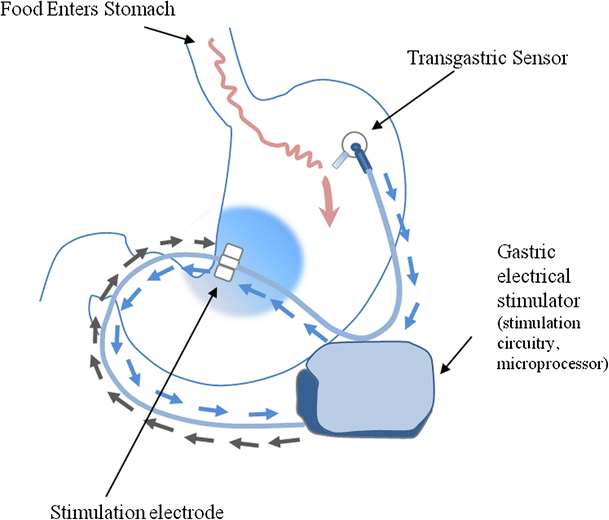
Gastric stimulator generator#
Ask your doctor exactly what you should expect during surgery and after the pulse generator is in place. Make sure you know what all of your other treatment choices are and that you and your doctor both feel that implanted vagus nerve stimulation is the best option for you. It's important to carefully consider the pros and cons of implanted vagus nerve stimulation before deciding to have the procedure. If side effects are intolerable, the device can be shut off temporarily or permanently. They may lessen over time, but some side effects may remain bothersome for as long as you use implanted vagus nerve stimulation.Īdjusting the electrical impulses can help minimize these effects. Some of the side effects and health problems associated with implanted vagus nerve stimulation can include:įor most people, side effects are tolerable. Vocal cord paralysis, which is usually temporary, but can be permanent.Pain where the cut (incision) is made to implant the device.Surgical complications with implanted vagus nerve stimulation are rare and are similar to the dangers of having other types of surgery. But it does have some risks, both from the surgery to implant the device and from the brain stimulation. Continue standard depression treatments along with vagus nerve stimulationĪdditionally, researchers are studying vagus nerve stimulation as a potential treatment for a variety of conditions, including headaches, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, bipolar disorder, obesity and Alzheimer's disease.įor most people, vagus nerve stimulation is safe.Haven't improved after trying four or more medications or electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), or both.Have chronic, hard-to-treat depression (treatment-resistant depression).The FDA has also approved vagus nerve stimulation for the treatment of depression in adults who: Have seizures that aren't well-controlled with medications.The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved vagus nerve stimulation for people who: Vagus nerve stimulation may also be helpful for people who haven't responded to intensive depression treatments, such as antidepressant medications, psychological counseling (psychotherapy) and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
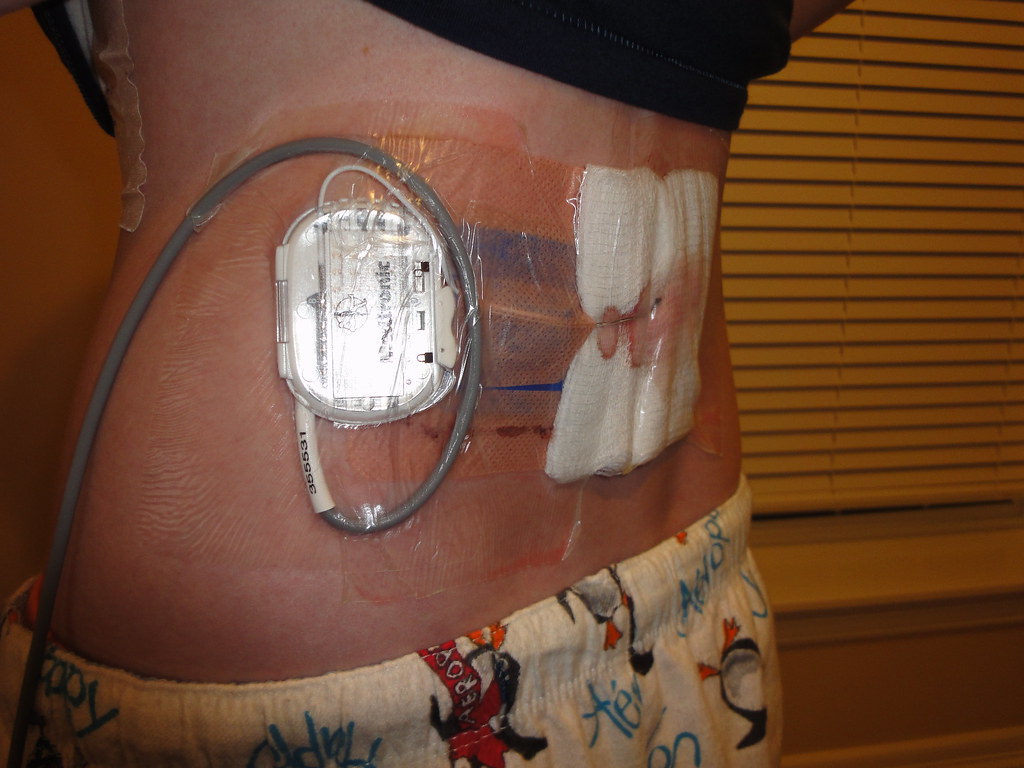
Vagus nerve stimulation may be an option to reduce the frequency of seizures in people who haven't achieved control with medications. In vagus nerve stimulation, an implanted pulse generator and lead wire stimulate the vagus nerve, which leads to stabilization of abnormal electrical activity in the brain.Ībout one-third of people with epilepsy don't fully respond to anti-seizure drugs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
